With the rapid development of industrialization, it is necessary to control the operation of equipment in various fields. One of the most important components in these devices is the IGBT chip. Effective thermal management is crucial to ensuring the reliable operation of IGBTs, making the design of liquid cooling plates for heat dissipation a significant topic.
The design of a liquid cooling plate is usually based on the power and operating conditions of the IGBT. When an IGBT has a power exceeding 1 kW, a dedicated liquid cooling plate is essential for its thermal management.
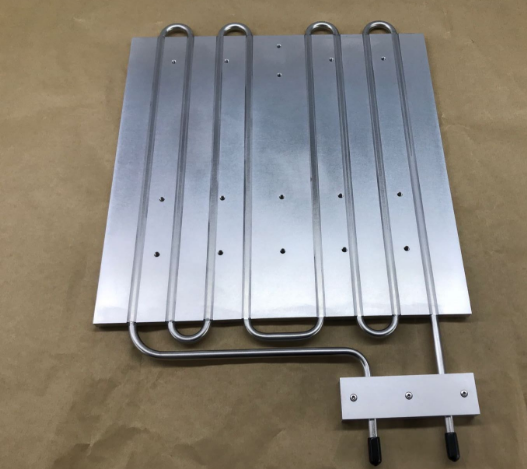
To design such a cooling plate, selecting appropriate processes and materials is key. For IGBTs with power below 1 kW, a cold plate with embedded copper tubes is typically used. For those above 1 kW, microchannel processing of the flow channels under the IGBT is generally required. Therefore, microchannels are often fabricated using skived fin processes, and the liquid cooling plate is produced by combining this with friction stir welding.
Regarding tube-embedded designs, the choice of tubes depends on the type of coolant used. Aluminum, copper, or stainless steel tubes can all serve as flow channels. Gaps between the tubes and the base plate are usually filled with epoxy resin, which helps achieve efficient heat dissipation.
In summary, designing a suitable liquid cooling plate involves considering numerous parameters and factors. It is essential to base the design on actual applications and find the optimal solution through continuous testing.