Thermal management of data centers
Thermal management is crucial for data centers. High - density servers generate vast amounts of heat. Effective systems, like advanced cooling units and optimized airflow designs, are essential to prevent overheating, ensuring stable operation and long - term reliability.
Our Businesses
Get a Quotation
What is a computer computing data center?
A computer processing center is a centralized place for large-scale data processing and computation. It is equipped with a large number of high-performance computer devices, such as servers, supercomputers, etc., which can quickly process various complex computing tasks through high-speed network connections,It not only includes computer calculation functions, but also focuses on data storage, management, and transmission. The data center has a massive amount of storage devices to store various data, while also having a well-established network infrastructure to ensure efficient transmission of data between different systems and users. In addition, data centers also need system level thermal management to ensure data security and continuous business operations, providing comprehensive data service support for enterprises, institutions, and others.
How is thermal management conducted in data centers?
The data center conducts thermal management through various collaborative methods to maintain stable equipment operation. The following is an introduction to how data centers conduct thermal management from three aspects: air cooling system, liquid cooling system, and immersion system:
Air cooling system
By installing air conditioning units in the data center, such as computer room air conditioning (CRAC), cold air is sent into the data center. By using elevated floor or ceiling ventilation ducts, cold and hot air channels are formed, allowing cold air to accurately reach the air inlet of servers and other equipment, while hot air is discharged through the hot channel, achieving cold and hot air isolation and improving cooling efficiency. Meanwhile, servers and other devices are also equipped with fans to assist in heat dissipation, accelerate air flow, and ensure timely dissipation of internal heat.
Liquid Cooling System
Divided into direct liquid cooling and indirect liquid cooling. Direct liquid cooling is the process of delivering coolant directly to the heating components of servers, such as CPUs, GPUs, etc., and removing heat through the circulation of the liquid. Indirect liquid cooling is the process of transferring heat to an intermediate medium and then cooling it with a coolant. Liquid cooling systems can handle high heat density issues more efficiently. Compared to air cooling, they can significantly reduce energy consumption, improve heat dissipation, and reduce local hotspots.
The liquid cooling system of Walmate Thermal generally uses copper liquid cooling plates as the core components for CUPs,GPUs cooling. The microchannels inside the copper liquid cooling plates are fabricated using the Skived fin process, followed by copper tube brazing to form a liquid cooling module, which is then connected to the entire cooling cycle system for chip cooling.


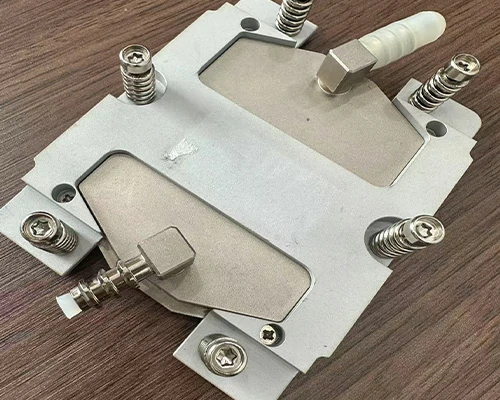
Immersion Cooling System
The Immersion cooling refers to the complete immersion of core equipment such as servers in non-conduAccording to whether the coolant undergoes a phase change during the circulation and heat dissipation process, it can be divided into single-phase immersion liquid cooling and two-phase immersion liquid cooling. Single phase immersion liquid cooled coolant typically has a high boiling point and does not undergo a phase change after absorbing heat. It is circulated through natural convection or pump driven cooling to transfer heat to an external heat exchanger for cooling. Dual phase immersion liquid cooling uses low boiling point coolant, and the heat generated by the equipment causes the coolant to boil, changing from liquid to gas. The steam rises to the condenser coil and condenses into liquid and flows back, utilizing the latent heat of phase change to achieve efficient heat dissipation.ctive inert coolant for heat dissipation.


Here are some timely articles written by our engineers during the actual application process for the design and reference of customer engineers:
- How to choose the coolant for a liquid cooling system?
- What a liquid cold plate for GPU?
- How to design microchannels for liquid cooled plates?
- What are the materials of liquid cooled plates?

